

<String Type> <string variable name> = "<sequence of string>"; e.g String exam= "DockerTpoint";
The "string constant pool" is checked first by the JVM whenever a string literal is created. A reference to the pooled instance of the string is returned if it already exists. If the string is missing from the pool, a new instance of the string is created and added to the pool.

String exam= "DockerTpoint"; String exam1="DockerTpoint"; //No new instance is created.
Java can use the String Literal to save memory (because no new objects are created if it exists already in the string constant pool).
// Java example of String Literal
public class Main { public static void main(String args[]){ String exam= "DockerTpoint"; String exam1="DockerTpoint"; System.out.println(exam); System.out.println(exam1); } }
Output:
DockerTpoint
DockerTpoint
With a new operator, the string can be allocated dynamically and declared. When a String is dynamically allocated, a new memory location in the heap is given to it. This string won't be included in the pool of String constants.
String str = new String("Examdeva");
You must "intern" this string if you want to keep it in the constant pool.
String interned = str.intern(); // the string will be added to the pool of string constants.
public class Main { public static void main(String args[]){ String str = "DockerTpoint"; //String Declared without using new operator System.out.println("str = " + str); String str1 = new String("DockerTpoint"); //String Declared using new operator System.out.println("str1 = " + str1); } }
Output:
str = DockerTpoint
str1 = DockerTpoint
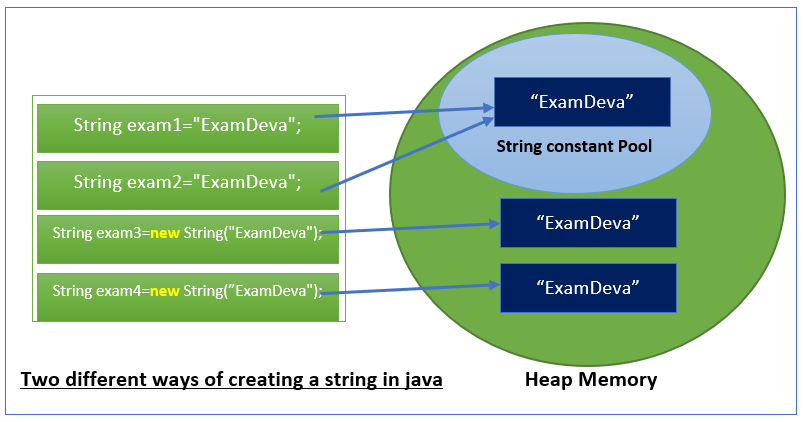
public class Main { public static void main(String args[]){ String exam1 = "DockerTpoint"; //string using string literal String exam2 = "DockerTpoint"; String exam3 = new String("DockerTpoint"); // strings using new keyword String exam4 = new String("DockerTpoint"); if(exam1 == exam2){ System.out.println("String exam1 and exam2 are equal"); } else{ System.out.println("String exam1 and exam2 are not equal"); } if(exam3 == exam4){ System.out.println("String exam3 and exam4 are equal"); } else{ System.out.println("String exam3 and exam4 are not equal"); } } }
Output:
String exam1 and exam2 are equal
String exam3 and exam4 are not equal
A peer class of String called StringBuffer offers many of the same features as strings. While StringBuffer represents expandable and writable character sequences, the string represents immutable, fixed-length character sequences.
StringBuffer str = new StringBuffer("DockerTpoint");
In Java, a mutable string of characters is represented by the StringBuilder class. The StringBuilder class offers a substitute for the String Class in Java because it generates mutable sequences of characters as opposed to the String Class's immutable ones.
StringBuilder sB = new StringBuilder(); sB.append("DockerTpoint");
A string can be divided into tokens using Java's StringTokenizer class. Internally, a StringTokenizer object keeps track of where it is in the string that needs to be tokenized. Some operations move this position ahead of the currently processed characters. By extracting a substring from the string that was used to create the StringTokenizer object, a token is returned.

Java supports immutable string objects.because Java makes use of the string literal concept. Let's say there are five reference variables, all of which refer to the same thing, "Sachin." All reference variables will be impacted if one reference variable alters the value of the object. Because of this, string objects in Java are immutable.
Post your comment